Welcome to the world of Web3, where cryptocurrencies, blockchain, and a unique culture converge. Entering the world of Web3 can be both thrilling and overwhelming, especially when faced with the seemingly cryptic language used by enthusiasts. Don't worry if you feel they sound like some secret codes, we are here to unravel their meaning. In this article, we are going to introduce [Private Data Attestation].
What is Private Data Attestation?
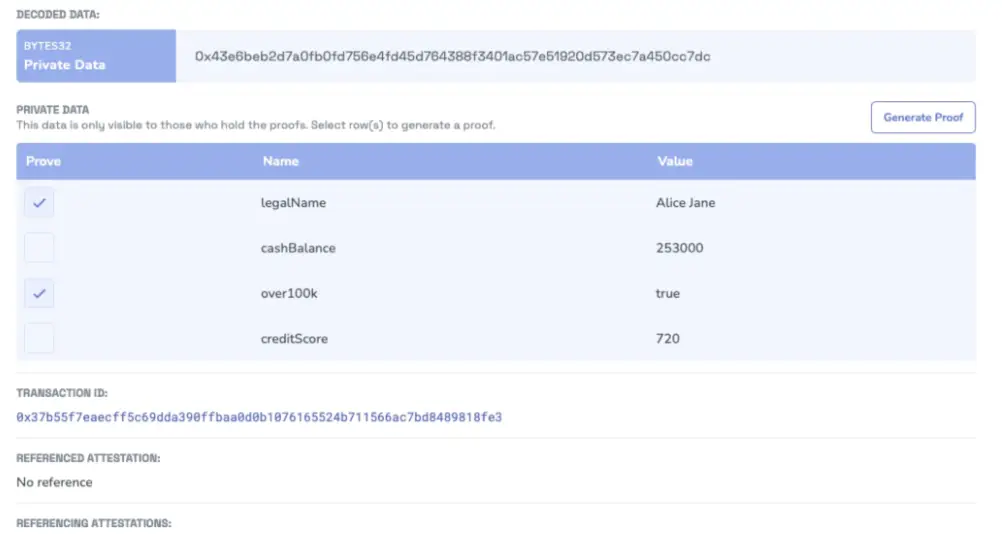
Private Data Attestation leverages the cryptographic structure of Merkle Trees to selectively reveal specific data fields while safeguarding the privacy of the entire dataset. By creating an attestation with a "private data" field containing the hash of a Merkle tree root, users can securely disclose particular data while keeping the rest confidential. This approach grants precise control over data sharing, which is invaluable when sensitive information needs to remain private while still verifying specific attributes or meeting regulatory requirements.
How does Private Data Attestation Work?
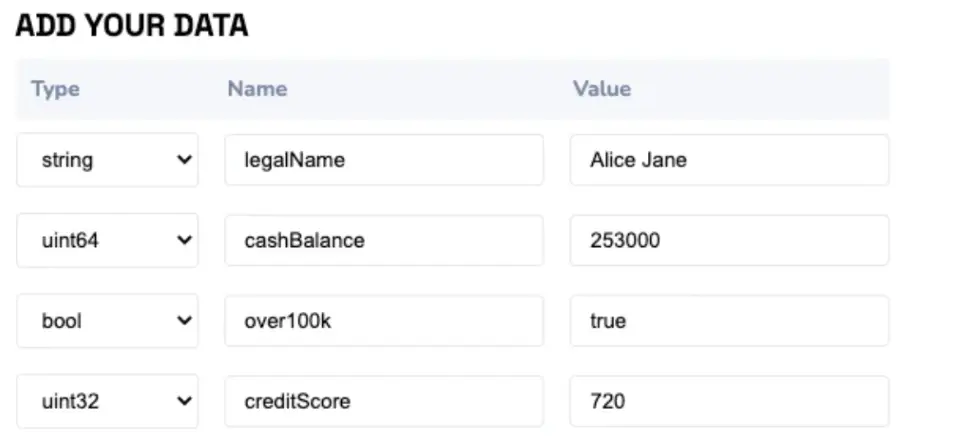
The process begins when a user submits data for selective disclosure using a privateData schema. This data is then encoded to generate a unique Merkle root hash that serves as an identifier for the dataset. The creator's address will attest to this root hash, either on-chain or off-chain, and the resulting attestation will contain a single "private data" field representing the root hash. When the user needs to share specific fields, they generate proofs for those data points. These proofs can be checked against the root hash, confirming the authenticity and inclusion of the data without revealing the entire dataset.
The Backstory of Private Data Attestation
Take the backstory of private data attestation as a discovery of the underlying technology of Merkle Trees, which is pivotal in balancing privacy with data integrity.
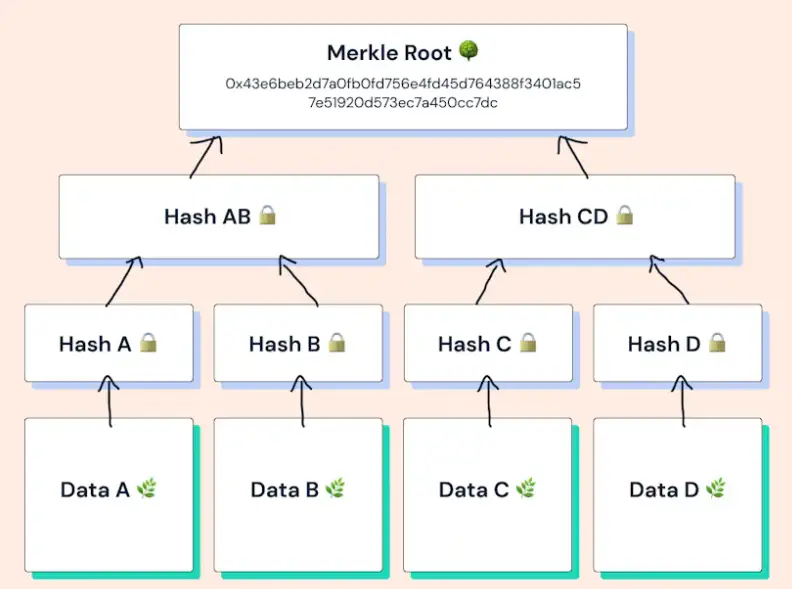
Each data element, called a "leaf," is hashed individually at the base of the tree. Pairs of these hashed leaves are then combined and hashed together, forming the next level of parent nodes. This process continues up the tree, layer by layer, until only one hash remains at the top, known as the Merkle Root.
With a Merkle proof, which contains a specific data element's hash and a series of related hashes, a verifier can confidently confirm the inclusion of a data field against the Merkle Root without needing access to the complete dataset.
The Use Case of Private Data Attestation
Private Data Attestations find their strength in scenarios where privacy must be maintained alongside the necessity to share information. Here are some use cases illustrating the versatility of this technology:
●Financial Services: In the financial sector, a bank can use private data attestations to confirm a client's cash balance and credit score while protecting their full financial history. The client can selectively disclose only the relevant information required for a specific purpose, like proving sufficient funds for a real estate purchase.
●Employment and Education: Organizations can confirm someone's employment history or academic credentials without revealing personal details or other sensitive information. This can be crucial during hiring processes or academic admissions.
●Healthcare: Medical institutions could use attestations to share patient data with specialists or insurance companies without compromising patient privacy or breaching regulations like HIPAA.
●Supply Chain Management: Companies can verify the authenticity of products at each stage of the supply chain without revealing proprietary information or sensitive business intelligence.
Private Data Attestations, built upon Merkle Tree cryptography, provide a comprehensive solution for secure data sharing. They ensure that sensitive information remains private while granting selective data disclosure for proof of identity, eligibility, or compliance. This technology unlocks new applications for identity verification, access control, and financial compliance while promoting a privacy-centric approach that aligns with the growing demands for data security.
Want to explore more about attestation? Check out HackQuest’s EAS Learning Track for more details and insights.