Back
Arbitrum Orbit
Arbitrum
By HackQuest
Apr 22,20243 min readWelcome to the Web3 world, where digital finance and applications are shown in a revolutionary way through the fusion of blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies, and a pioneering spirit. Are you overwhelmed by the wealth of terms in the Web3 world that you don’t understand? Are those slang barriers for you to learn about Web3? Don’t worry! We’re here to explain the obscure terms to guide your learning. Today, we're diving into an exciting development in the world of Ethereum scaling solutions: [Arbitrum Orbit].

Overview
Arbitrum Orbit, introduced by Arbitrum in March 2023, gives users the tools to create their own Layer 3 (which is a layer on top of the Ethereum mainnet Layer 1 and Layer 2, so it's called Layer 3). Think of these as custom-made chains designed to fit exactly what you need for your projects or business. It lets users pick whether they want to use Rollup technology (like what's in Arbitrum One) or AnyTrust technology (like in Arbitrum Nova) to set up their Orbit chains. Plus, you can tweak things to your liking, including privacy settings, who gets to access, what kind of fees to use, how it's governed, and lots more. There's a diagram that shows how Layer 1, Layer 2, and Layer 3 relate to each other:
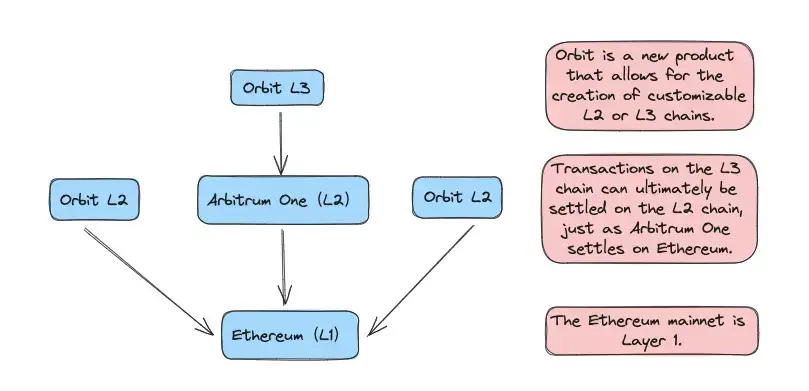
Why Orbit - Advantages
Arbitrum One and Arbitrum Nova are owned and managed by the Arbitrum DAO. They are public chains and are widely used by many users to fulfill their needs. But some people may not prefer shared public chains as they are bounded by regulations. While with Orbit chain, you can decide how your chain is governed.
Dedicated Throughput
If your decentralized app (dApp) needs lots of power or always available resources, you might want a setup where you don't have to share. Having your dApp on its own Orbit chain means you get all the resources to yourself, without having to fight over computer and storage space.
Better Compatibility with EVM+
Orbit chains will work great with the new EVM+ compatibility that comes with Stylus (we'll talk more about this later). You'll be able to use smart contracts that work with EVM using languages like Solidity, C, C++, and Rust, all without having to switch from your current programming language.
Independent Product Roadmap
With Orbit, you can take your app's development in a different direction from what Ethereum or Arbitrum is doing. You can add new features, like making accounts more flexible, faster than waiting for those changes to happen on the public Ethereum network.
Stable Transaction Costs
For many dApps, knowing how much transactions will cost is important. Since Orbit chains are separate from the busy Arbitrum L2 and Ethereum L1, your dApp won't be thrown off by what's happening elsewhere, giving your users more stable gas prices.
Custom Gas Tokens
On Orbit chains, you can choose different ERC-20 tokens to pay for gas, making it easier to match your app's ecosystem. This option is ready to go for AnyTrust chains. ERC-20 tokens are based on a common standard that sets up the basics for tokens, like transferring them, checking balances, and the total amount of tokens available.
Flexible Technological Options
Orbit lets you choose from Rollup, AnyTrust, or even your own tech setup. This flexibility means you can use just the tech pieces that fit your project best, making Ethereum and Arbitrum tech bend to your needs.
Conclusion
Arbitrum Orbit represents a significant advancement in the blockchain domain, offering the flexibility to create Layer 3 chains tailored to specific needs and preferences since its launch in March 2023. It empowers users with the choice between Rollup and AnyTrust technologies, along with extensive customization options such as privacy settings, access permissions, and governance models. Orbit's distinct advantages include dedicated throughput for resource-intensive dApps, EVM+ compatibility for a wide range of programming languages, and the ability to craft an independent product roadmap. Additionally, it ensures stable transaction costs and the option to use custom gas tokens, enhancing the overall dApp experience.
💡
If you would like to learn more about slang in Web3, let’s explore more in our HackQuest Web3 Glossary and check out our courses on Arbitrum Orbit!