Welcome to the Web3 world, where digital finance and applications are shown in the revolutionary way through the fusion of blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies, and a pioneering spirit. Are you overwhelmed by the wealth of terms in the Web3 world that you don’t understand? Are those slangs barriers for you to learn about Web3? Don’t worry! We’re here to explain the obscure terms to guide your learning. Today, we're diving into an exciting development in the world of Ethereum scaling solutions: [Arbitrum Nitro].
To learn about Arbitrum Nitro, we have to start with Arbitrum. In short, Arbitrum is an L2 scaling solution for Ethereum that offers a unique combination of benefits. 💡
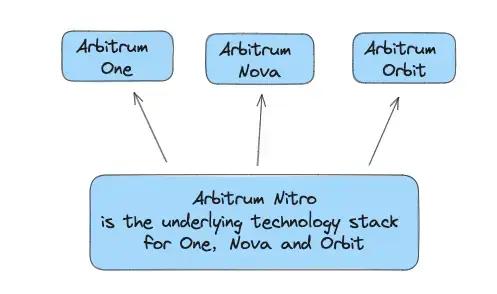
You can read more about Arbitrum in another glossary article. Arbitrum Nitro is NOT considered as a separate network, but a technical stack upgrade of Arbitrum One. The switch to Nitro was smooth, and the only things users really saw were lower costs, more room for transactions, and a quicker system. Even after updating to Nitro, people still call it Arbitrum One.
The Nitro upgrade supports not just the One network, but also the Nova and Orbit networks. This update was a big technical upgrade forward that the Arbitrum team achieved in 2022.
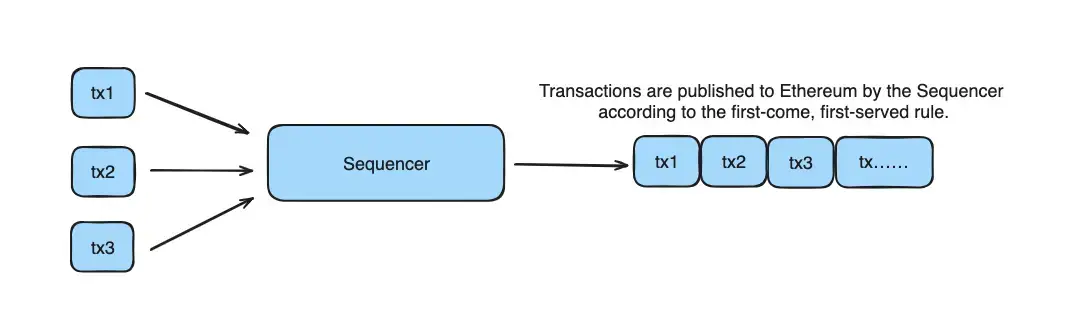
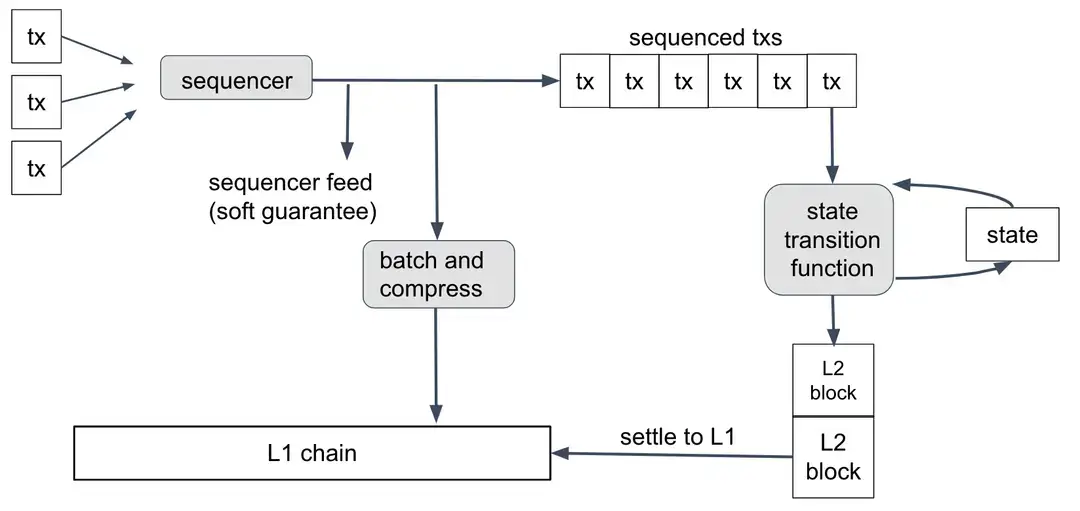
In Arbitrum, a Sequencer is a special kind of computer that decides the order in which transactions happen. Different from Ethereum, where how much you pay influences when your transaction goes through, the Arbitrum Sequencer lines transactions up in the order they come in, putting them in a queue before they go to L1. This queue takes the place of the usual mempool. If transactions in the Sequencer don't get done in time, they will run out of time and get thrown out.
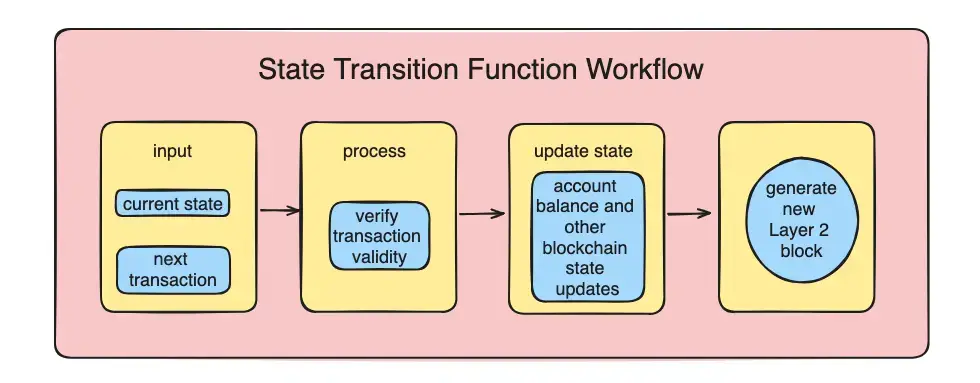
State Transaction Function
The state transition function is key in Arbitrum Nitro, handling every transaction on the network and bringing the blockchain's state up to date. Here's how it works:
Arbitrum Nitro brought four major innovations compared to Arbitrum One that solves some of the original problems Arbitrum One has.
Innovation 1: Sequencing + Deterministic Execution
1.First Phase: Self-Processing on Layer2
At this stage, the transaction hasn't been sent over to Ethereum yet and can still be changed, making it a "soft confirmation." But for users, it is technically complete, even though there are more following steps to ensure security.
1.Second Phase: Acquiring the Transaction Sequence
Sequencer publishes the transaction sequence in two ways: through real-time updates and by putting batches on the Ethereum blockchain.
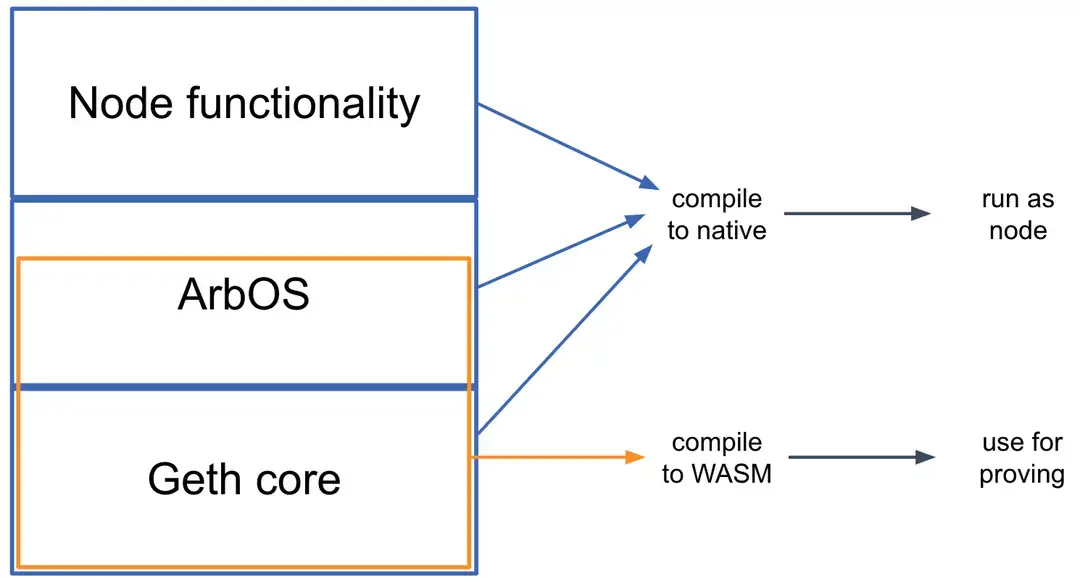
Innovation 2: Geth as the Core Foundation
1.Bottom Layer: This is the heart of Geth, taking care of mimicking how EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) contracts run and keeping track of Ethereum's state information. 2.Middle Layer: This is where ArbOS comes in. It does things like sort through data batches from the sequencer, figure out the gas costs on Layer 1, and gather up fees to cover those costs.
3.Top Layer: Mostly made up of node software from Geth, this part deals with connecting to users and handling their RPC (remote procedure call) requests, along with other complex tasks needed to keep a blockchain node that works with Ethereum running smoothly. Innovation 3: Separation of Execution and Verification
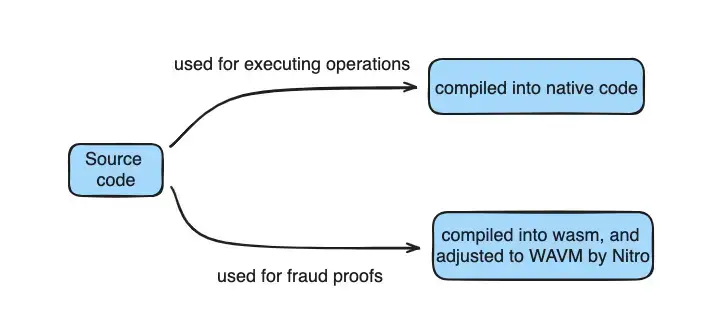
When Nitro comes to checking for any cheating or errors (fraud proofs), that code is turned into a special binary format called wasm. Nitro has tweaked this wasm format a bit to work better with blockchain stuff, and they call this tweaked version WAVM code. If anyone's not sure whether an operation's outcome is right, they can use this WAVM code to check it.
Innovation 4: Interactive Fraud Proofs
Interactive fraud proofs are a way to resolve resolution by asking participants to reduce their disagreements through a series of steps, till only one specific argument remains. This system tries to settle fights off the blockchain by getting people involved to talk it out as much as they can, and it only asks the blockchain to step in when there's one specific thing left to sort out.
With the four innovations, Nitro positions itself with core advantages:
●Better EVM Fit: Nitro matches up more closely with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) because it uses Geth right out of the box.
●Making Things Easier: By leveraging the existing Geth software, Nitro reduces the workload required to create an L2 virtual machine. Now, code can be written in Go instead of a custom language, making it easier to understand and audit.
●Cutting Costs: Nitro separates the doing from the checking, meaning it only switches to Wasm bytecode when there's an argument about the results. Usually, it just runs on the Go code the node has, which makes things run smoother and cheaper for everyone.
●Data Compression: Through broadly tested compression libraries, Nitro helps users to cut cost of posting data on Ethereum.