Back
Off-Chain Attestation
EAS
By HackQuest
May 27,20243 min readWelcome to the world of Web3, where cryptocurrencies, blockchain, and a unique culture converge. Entering the world of Web3 can be both thrilling and overwhelming, especially when faced with the seemingly cryptic language used by enthusiasts. Don't worry if you feel they sound like some secret codes, we are here to unravel their meaning. In this article, we are going to introduce [Off-Chain Attestation].
What is Off-Chain Attestation?
Attestations are digital verifications crucial for confirming the authenticity, ownership, or validity of information. This is particularly important in an era increasingly dominated by AI-generated synthetic content, such as deepfakes, which threaten public trust and personal reputation. Off-chain attestation refers to attestations that are performed outside the blockchain but can be linked to blockchain technology for additional security and verification capabilities.
How does Off-Chain Attestation Work?
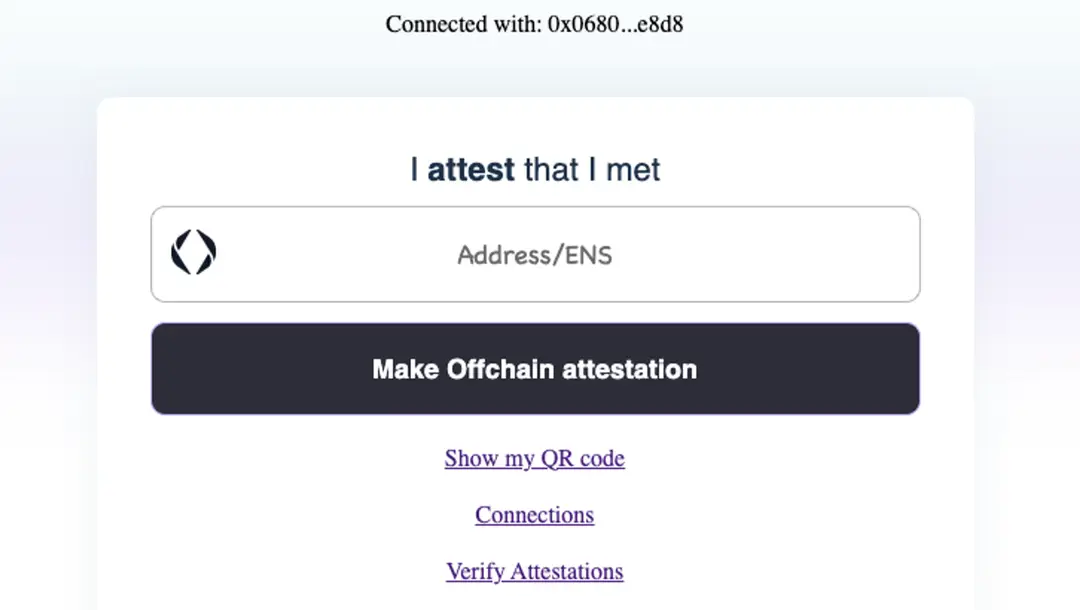
Off-chain attestation involves validating data or transactions without recording the information directly on a blockchain. This process typically uses cryptographic techniques to ensure data integrity and authenticity while keeping the attested data off the blockchain to ensure privacy and scalability. Steps include creating a digital signature, generating a QR code, or issuing a peer-to-peer (P2P) shareable link. Such attestations can be verified through dedicated platforms or services that support off-chain verification methods.
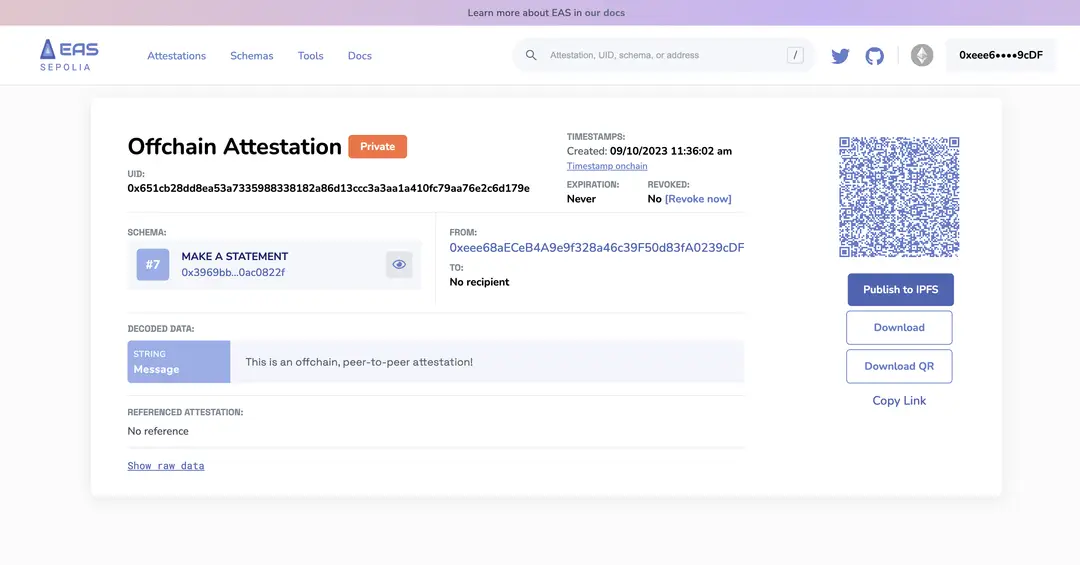
The Backstory of Attestation and Off-Chain Attestation
Historically, attestation involved the verification of facts or claims, often requiring a witness to validate documents or statements—akin to "witnessing" or providing "testimony." This traditional approach has seen a revolutionary shift with the advent of blockchain technology, which introduced the concept of on-chain attestation. Off-chain attestation emerged as a response to the need for privacy and efficiency in scenarios where the permanent recording of data on a blockchain is undesirable or unnecessary.
💡
Implications of Off-Chain Attestation
The implications of off-chain attestation are significant in terms of privacy, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. By not recording every transaction on the blockchain, off-chain attestations reduce network congestion and eliminate the costs associated with blockchain transactions, such as gas fees. This approach also allows for the attestation of sensitive data without exposing it on a public ledger, thus maintaining confidentiality. Below are some practical use cases that highlight the advantages of off-chain attestation:
1.Identity Verification in Financial Services:
Financial institutions can use off-chain attestations to verify the identity and financial history of clients without storing personal information on a public blockchain. This ensures compliance with privacy regulations while providing a secure and efficient verification process.
2.Healthcare Data Sharing:
Off-chain attestation can facilitate the secure and private sharing of medical records between healthcare providers. By using off-chain methods, sensitive health information can be attested to for accuracy and completeness without being exposed on a public ledger, ensuring patient privacy.
3.Supply Chain Traceability:
Companies can use off-chain attestations to verify the origin and handling of goods in a supply chain without revealing proprietary or sensitive business information on a blockchain. This method enhances transparency and trust among stakeholders while protecting business confidentiality.
4.Digital Media Rights Management:
Artists and creators can utilize off-chain attestations to prove ownership and distribution rights of digital media such as music, videos, and artwork. This allows for the secure sale and transfer of rights without the need for public disclosure of each transaction.
5.Voting Systems:
Off-chain attestations can create secure and private voting systems where votes are verified for authenticity without being individually recorded on the blockchain. This maintains voter anonymity and election integrity.
Conclusion
Off-chain attestations offer a unique blend of privacy, efficiency, and flexibility, making them suitable for a variety of use cases where blockchain's transparency is not desired. Whether used for personal or professional purposes, off-chain attestations provide a versatile tool for digital verification in the modern age. Check this out to attest your knowledge about attestation!