Back
Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS)
Vara Network
By HackQuest
Jun 28,20243 min readWelcome to the Web3 world, where digital finance and applications are shown in a revolutionary way through the fusion of blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies, and a pioneering spirit. Are you overwhelmed by the wealth of terms in the Web3 world that you don’t understand? Are those slangs barriers for you to learn about Web3? Don’t worry! We’re here to explain the obscure terms to guide your learning. Today, we're diving into an innovative development in the world of Web3: [Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS)].
Definition and Overview
Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS) is a consensus mechanism designed to secure blockchain networks by leveraging the power of stakeholder participation. It is a variation of the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) mechanism, wherein validators are selected based on their stake and nominations from other stakeholders. NPoS aims to enhance decentralization, security, and fairness in the selection of validators.
Technical Composition
Nominated Proof-of-Stake involves several key components that ensure its efficient and secure operation:
●Validators: Validators are responsible for producing new blocks and securing the network. They are selected based on their stake and the nominations they receive from other stakeholders.
●Nominators: Nominators are stakeholders who support specific validators by nominating them. They stake their tokens to back validators they trust, influencing their chances of being selected.
●Staking: Both validators and nominators stake their tokens as collateral. If validators act maliciously or fail to perform their duties, they and their nominators can lose a portion of their staked tokens (slashing).
●Election Mechanism: Validators are elected through a transparent and decentralized process, ensuring that those with the highest combined stake (own stake plus nominations) are selected.
Core Functions
1.Security: NPoS enhances network security by involving a wide range of stakeholders in the selection of validators, reducing the risk of centralization and attacks.
2.Decentralization: By allowing nominators to participate in the selection process, NPoS ensures a more decentralized and democratic validation mechanism.
3.Incentivization: Validators and nominators are incentivized to act honestly and efficiently through staking rewards and penalties for malicious behavior.
Use Cases
Blockchain Security
Description: NPoS is used to secure blockchain networks by selecting trustworthy validators through a decentralized and transparent process.
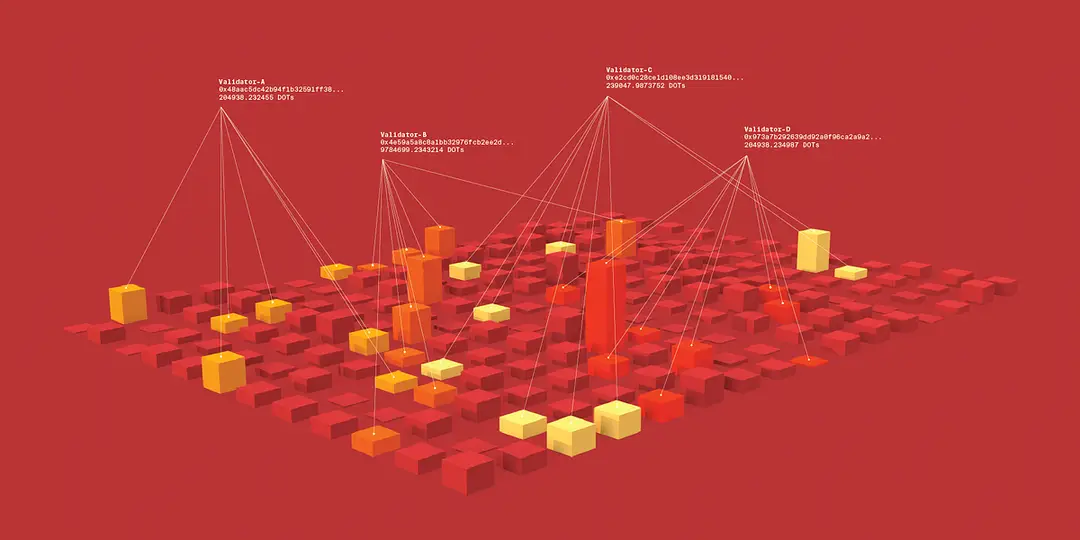
Examples: Polkadot and Kusama networks use NPoS to secure their blockchains, ensuring that only the most reliable and well-supported validators are chosen.
Source: Polkadot
Advantages: Enhances security and decentralization, reducing the risk of attacks and centralization of power.
Validator Selection
Description: The NPoS mechanism selects validators based on their stake and nominations, ensuring a fair and decentralized selection process.
Examples: Validators on the Polkadot network are selected through NPoS, where stakeholders nominate and support validators they trust.
Advantages: Promotes fairness and transparency in the selection of validators, encouraging widespread participation from stakeholders.
Staking and Rewards
Description: NPoS incentivizes stakeholders to participate in the network by offering staking rewards to both validators and nominators.
Examples: Nominators on the Kusama network receive a portion of the staking rewards earned by the validators they support.
Advantages: Provides financial incentives for stakeholders to contribute to the network's security and decentralization.
Source: Medium
Importance in Web3 Ecosystem
Nominated Proof-of-Stake plays a crucial role in the Web3 ecosystem by ensuring the security, decentralization, and efficiency of blockchain networks. It promotes a more democratic and transparent selection process for validators, encouraging broad participation from stakeholders. This mechanism enhances the overall resilience and trustworthiness of decentralized networks.
User Experience and Innovations
NPoS focuses on delivering a seamless user experience by providing intuitive interfaces for staking, nominating, and participating in network governance. Innovations such as user-friendly staking platforms and transparent election mechanisms ensure that stakeholders can easily engage with the network and contribute to its security and decentralization.
Challenges
Despite its advantages, Nominated Proof-of-Stake faces challenges such as ensuring the security and reliability of the staking process, maintaining decentralization while scaling, and achieving widespread adoption. Continuous development and rigorous testing are essential to address these challenges and ensure the protocol’s long-term success.
Conclusion
Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS) represents a significant advancement in blockchain consensus mechanisms, offering a secure, scalable, and efficient method for validating transactions and securing networks. By involving a broad range of stakeholders in the selection process, NPoS enhances decentralization and promotes a more democratic and transparent blockchain ecosystem. Understanding and leveraging NPoS is essential for anyone involved in Web3 and decentralized finance.