Back
Data Availability
Dev
By HackQuest
May 10,20246 min readWelcome to the world of Web3, where cryptocurrencies, blockchain, and a unique culture converge. Entering the world of Web3 can be both thrilling and overwhelming, especially when faced with the seemingly cryptic language used by enthusiasts. Don't worry if you feel they sound like some secret codes, we are here to unravel their meaning in Web3 context. In this article, we are going to introduce [Data Availability].

What Does 'Data Availability' Mean?
Data availability refers to the ability of all participants in a blockchain network to access and verify the data necessary to maintain the network's integrity and security. It ensures that the information required to validate transactions and blocks is readily accessible to anyone in the network, preventing fraud and ensuring transparency.
The Origins of Data Availability
As blockchain networks like Ethereum began to scale, they encountered challenges related to data storage and accessibility. With the blockchain's size growing continuously, ensuring that all participants can access complete and accurate data became a concern. This is especially true in the context of Layer 2 scaling solutions and sharded blockchains, where data might be processed or stored off the main chain. Ensuring data availability in these contexts is crucial for maintaining the security and operability of the network.
🚀
Check out: What is the meaning of Lay 2?
How Does Data Availability Work?
Mechanism: In a blockchain network, data (transactions, smart contracts, etc.) is bundled into blocks. For a block to be added to the chain, it must be validated by network participants (nodes). Data availability comes into play here, as nodes must be able to access the block's data to verify its validity.
There are several approaches to ensuring data availability:
Fraud Proofs:
Systems that rely on fraud proofs require data to be available so that participants can challenge invalid transactions or blocks after they have been added to the chain.
Data Sharding:
Sharding divides the network into smaller segments (shards), each responsible for processing a fraction of the transactions. This approach requires a robust data availability mechanism to ensure that data is accessible across shards and can be reconstructed if needed.
Erasure Coding:
This method involves breaking data into fragments, encoding it with redundant pieces, and distributing it across the network. Even if some fragments are missing, the original data can be reconstructed from the available pieces, ensuring data availability.
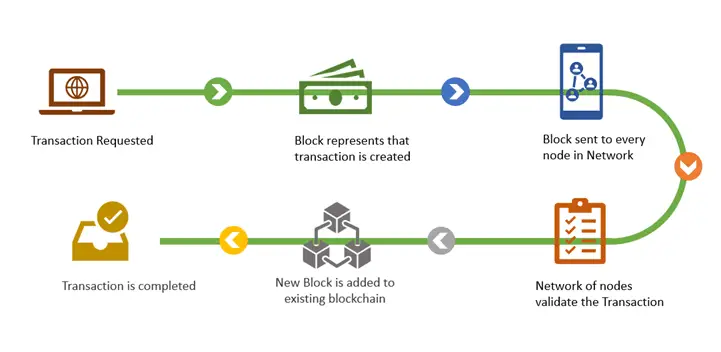
Source: Medium
Why is Data Availability Important?
Security and Integrity
Ensuring that data is available and accessible to all network participants is crucial for maintaining the security and integrity of the blockchain. It prevents malicious actors from manipulating or withholding data to undermine the network.
Decentralization
Data availability supports the decentralized nature of blockchain by allowing all participants to independently verify transactions and blocks, rather than relying on a central authority.
Scalability
Effective data availability solutions are key to scaling blockchain networks. They allow for more complex architectures, like sharded blockchains and Layer 2 solutions, by ensuring that the network remains secure and verifiable, even as it grows in size and complexity.
Examples of Data Availability Solutions
Ethereum's transition to Ethereum 2.0 introduces sharding as a scalability solution, which relies heavily on ensuring data availability across shards. Another example is the use of rollups (Optimistic and ZK-Rollups) as Layer 2 solutions, where data availability ensures that the state of the rollups can always be verified against the main chain.
📢
Conclusion
Data availability is foundational to blockchain technology and Web3, ensuring that networks remain secure, transparent, and decentralized. As the ecosystem continues to evolve, finding scalable and efficient solutions for data availability will be crucial for developing more complex, scalable, and user-friendly decentralized applications. Understanding the role and mechanisms of data availability is essential for anyone looking to navigate or contribute to the Web3 space.
If you would like to learn more about slang in Web3, let’s explore more in our HackQuest Web3 Glossary!