Back
Causal Order
Sui
By HackQuest
Aug 28,20242 min readWelcome to the Web3 world, where digital finance and applications are shown in a revolutionary way through the fusion of blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies, and a pioneering spirit. Are you overwhelmed by the wealth of terms in the Web3 world that you don’t understand? Are those slang barriers for you to learn about Web3? Don’t worry! We’re here to explain the obscure terms to guide your learning. Today, we're diving into an innovative development in the world of Web3: Causal Order.
Definition and Overview
Causal Order refers to the sequence and relationship between transactions and the objects they generate, presented as dependencies. In a blockchain context, this means validators must execute transactions in a specific order to respect these dependencies. Unlike total order, where every transaction is sequentially ordered, Sui blockchain uses causal order, which is a partial order that respects the dependencies among transactions without imposing a strict sequential order.
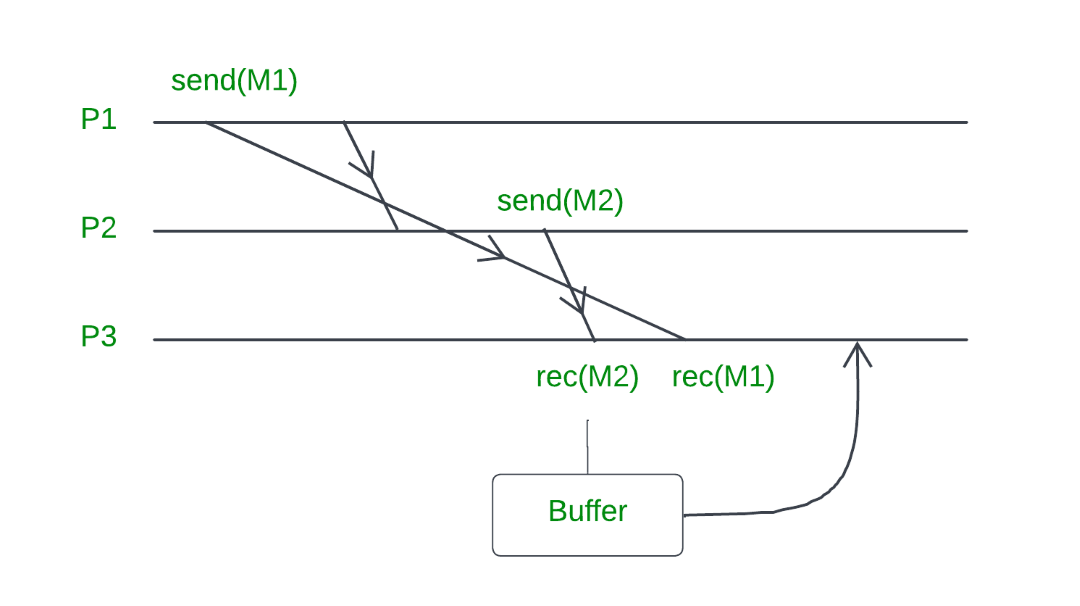
Source : GeeksforGeeks
Technical Composition
Causal order in blockchain involves the following components:
1.Transactions and Objects: Each transaction can create or modify objects, and subsequent transactions may depend on these objects.
2.Validators: Nodes in the network that validate transactions based on the dependencies.
3.Dependencies: The relationships between transactions and the objects they affect, which must be respected during execution.
In practical terms, validators cannot execute a transaction that depends on objects created by a previous transaction until that prior transaction has been completed. This ensures the integrity and consistency of the blockchain.
Core Functions
1.Dependency Tracking: Ensures that transactions are executed in an order that respects their dependencies.
2.Partial Order: Allows for parallel execution of transactions that do not depend on each other, enhancing scalability.
3.Consistency: Maintains the integrity of the blockchain by ensuring all dependencies are respected.
Use Cases
1.Smart Contracts: Ensuring that functions dependent on previous state changes execute correctly.
2.DeFi Platforms: Managing complex financial transactions with multiple dependencies efficiently.
3.Supply Chain Management: Tracking the movement and ownership of goods where transactions depend on prior states.
Importance in Web3 Ecosystem
Causal order is crucial in the Web3 ecosystem for several reasons:
1.Efficiency: By allowing parallel execution of independent transactions, it improves the throughput and performance of the blockchain.
2.Scalability: Reduces bottlenecks associated with sequential transaction processing.
3.Integrity: Ensures that the blockchain state remains consistent and reliable.

Source : Cointransend
Conclusion
Causal order represents a significant advancement in blockchain technology, providing a framework for more efficient, scalable, and reliable transaction processing. By respecting dependencies between transactions, it ensures the integrity of the blockchain while allowing for parallel execution where possible.
In conclusion, causal order exemplifies the innovative potential of Web3, offering a sophisticated solution to the challenges of transaction processing in a decentralized world. As the technology continues to evolve, its adoption and refinement will likely drive further advancements in the scalability and efficiency of blockchain platforms, solidifying its role as a cornerstone of the future decentralized web.