Back
Arbitrum One
Arbitrum
By HackQuest
Apr 22,20243 min readWelcome to the world of Web3, where cryptocurrencies, blockchain, and a unique culture converge. Entering the world of Web3 can be both thrilling and overwhelming, especially when faced with the seemingly cryptic language used by enthusiasts. Don't worry if you feel they sound like some secret codes, we are here to unravel their meaning in Web3 context. In this article, we are going to introduce [Arbitrum One].

What Is 'Arbitrum One'?
Acting as the original and most popular Layer 2 option, Arbitrum One is known as the flagship chain of the Arbitrum ecosystem. Through the Optimistic Rollups technology mentioned earlier, Arbitrum One significantly increases transaction speed (Transactions Per Second) and cost-efficiency compared to Ethereum.
Arbitrum One focuses on DeFi and NFT projects. DeFi represents a blockchain-based financial ecosystem created to establish decentralized financial services and instruments, aiming to supplant conventional financial entities and middlemen. It seeks to offer more accessible and transparent financial services, encompassing aspects like lending, debt markets, stablecoins, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), liquidity mining, and more.
NFTs are digital assets that symbolize unique or non-fungible items or digital content. This includes digital art, virtual real estate, collectibles, music, etc.
Arbitrum Virtual Machine (AVM)
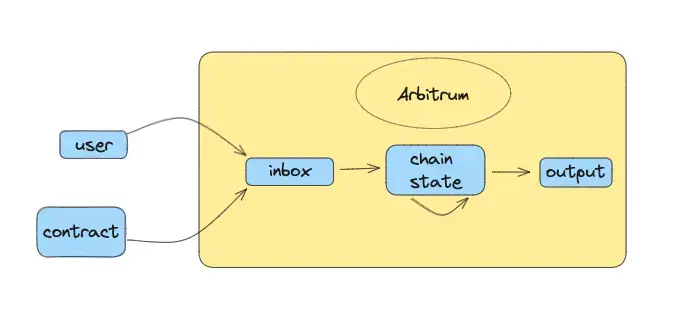
The Arbitrum Virtual Machine (AVM) is made just for Arbitrum to handle and run things on the Arbitrum Classic network. Think of a virtual machine (VM) in the blockchain world as a computer program that lets other programs run, especially the ones that deal with blockchain contracts.
There's only one AVM for each Arbitrum network. It works in a pretty straightforward way: it looks at the messages it gets, changes the network based on these messages (all these messages are also saved on the Ethereum blockchain), and then does what it needs to do next. The AVM was built to work a lot like the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), which means it can run programs made for the EVM without much trouble, keeping some of the main ideas of how the EVM is built.
ArbOS
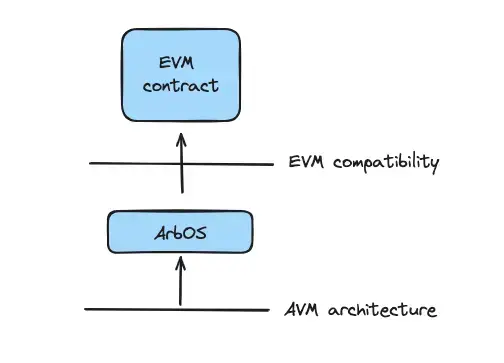
ArbOS is a special software made by Offchain Labs that takes care of all the logic and state updates for Arbitrum to work. It's named ArbOS because it works a lot like the system that runs your computer or phone, starting things up and then keeping other programs running on the network.
How Code is Processed and Executed in Arbitrum One
1.When you write code in high-level programming languages like Solidity or Vyper, it gets turned into a special code called EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) bytecode, kind of like preparing it to run on Ethereum.
2.Next, ArbOS takes this EVM bytecode and changes it into AVM (Arbitrum Virtual Machine) instructions. These instructions do two big things: they help the L2 virtual machine work, and they can show if someone's trying to cheat in case there's a disagreement (we'll dive deeper into this with Arbitrum Nitro, but for now, just remember that in AVM, the regular code and the cheat-catching code are the same thing).
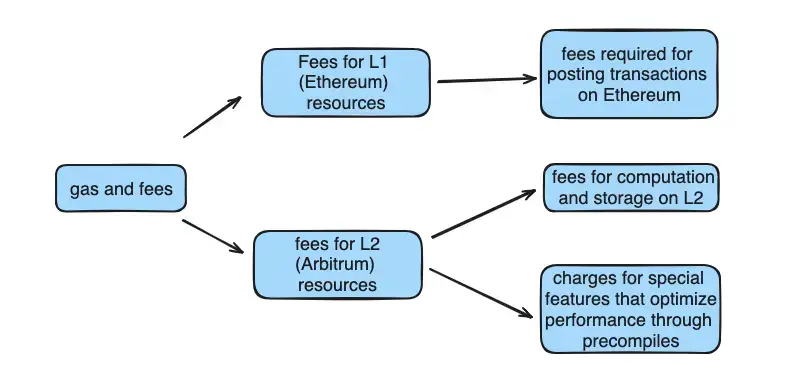
When you process transactions on Arbitrum One, there are two kinds of costs you need to consider: the costs for using L1 (Ethereum mainnet) and the costs for using L2 (which is Arbitrum).
Data Compression
Arbitrum's special virtual machine (AVM) is made just for Arbitrum. If you want to compress data in AVM, you have to develop a customized compression algorithm.
💡
There are more problems with the first version of Arbitrum One, and you can learn more in our online courses.
Problems with Arbitrum One
1.Performance and Scalability Limitations: Arbitrum One has made transactions faster and cheaper, but as more people use it and more transactions happen, it starts to run into problems with keeping up and growing.
2.High Transaction Fee: Arbitrum One tries to make fees lower, but when the network gets really busy, users might still end up paying a lot.
3.Complex Development and Maintenance: The Arbitrum Virtual Machine (AVM) that Arbitrum One uses is unique to it. This means programmers have to learn new tools and ways of coding, which makes building and keeping things running more complicated.
4.Limited EVM Compatibility: Arbitrum One works hard to be like the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), but some differences (like how it figures out gas costs and confirms blocks) can make moving and running certain smart contracts tricky.
5.Inconsistent Gas Pricing: How Arbitrum One figures out gas costs can be different from the main Ethereum network, which might confuse people who make and use apps.
💡
If you would like to learn more about slang in Web3, let’s explore more in our HackQuest Web3 Glossary and check out our courses on Arbitrum One!