Back
Arbitrum Nova
Arbitrum
By HackQuest
Apr 22,20244 min readWelcome to the Web3 world, where digital finance and applications are shown in a revolutionary way through the fusion of blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies, and a pioneering spirit. Are you overwhelmed by the wealth of terms in the Web3 world that you don’t understand? Are those slang barriers for you to learn about Web3? Don’t worry! We’re here to explain the obscure terms to guide your learning. Today, we're diving into an exciting development in the world of Ethereum scaling solutions: [Arbitrum Nova].

Overview
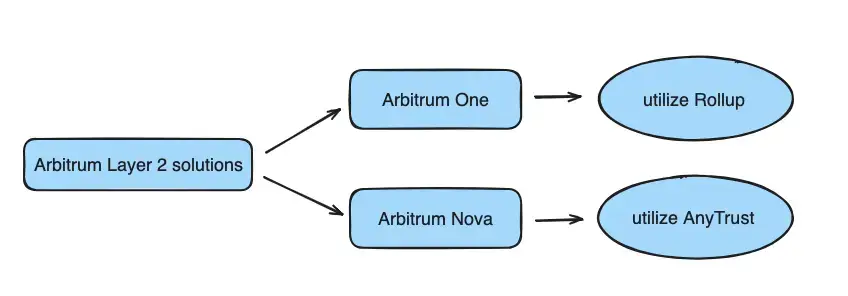
Arbitrum Nova is a different Layer 2 option in the Arbitrum family that has different use case than Arbitrum One. Arbitrum Nova uses something called AnyTrust technology. This method is centered around forming a group you can count on, known as the Data Availability Committee. With the help of this group to keep track of transaction details, we give up a little bit of decentralization to get better speed and efficiency. This trade-off is especially good for areas where quick and cost-effective solutions are key, like in gaming, social media, and simple financial tools.
Data Availability Committees and AnyTrust
Data Availability Committee
The Data Availability Committee is made up of approved nodes. This team takes care of holding onto and looking after data on the blockchain. They're the ones who make sure this data is available to other parts of the network whenever it's needed.
AnyTrust
AnyTrust is a twist on the Nitro tech setup that introduces a little bit of trust to help bring down costs.

Source: Medium
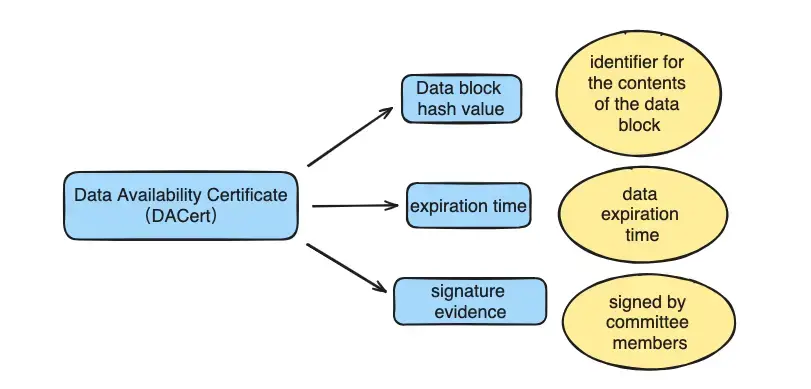
Data Availability Certificate (DACert)
A Data Availability Certificate (DACert) is a unique kind of proof that shows a block of data is trustworthy and can be gotten to. This proof is made up of three big pieces:
1.The data block's hash value: This acts like a tag that tells you what's in the data block.
2.Expiration time: Up until this moment, the data is guaranteed to be available.
3.Signature proof: This bit confirms that almost all (N-1 members) of the committee have put their signature on the hash value of the data block and when it's supposed to run out.
Data Availability Servers
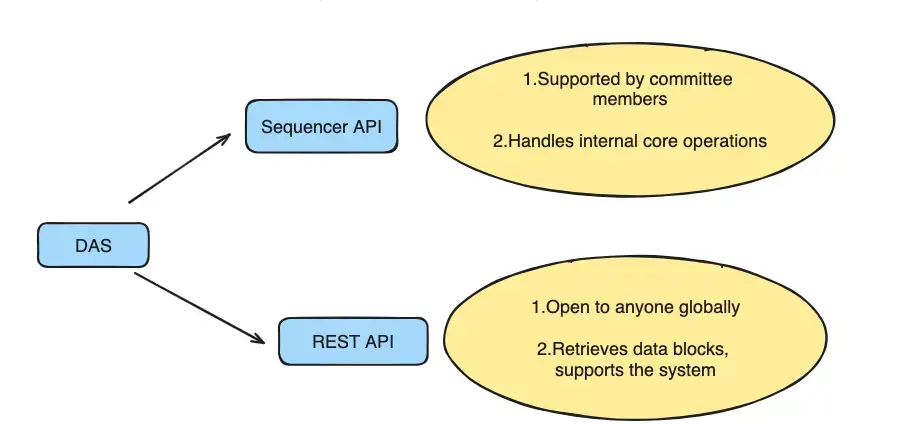
Data Availability Servers (DAS) are programs that committee members use to keep and get data from the blockchain. DAS provides two primary methods for connecting with the outside world:
1.Sequencer API: A special setup made for the Sequencer on Arbitrum. It lets the Sequencer send data blocks to be stored in DAS. To keep things safe, this setup is typically limited to just the Sequencer, blocking others who shouldn't get in.
2.REST API: An interface that anyone around the world can use to pull up data blocks by using their hash values.
The collaboration mechanism between the Sequencer and the Committee
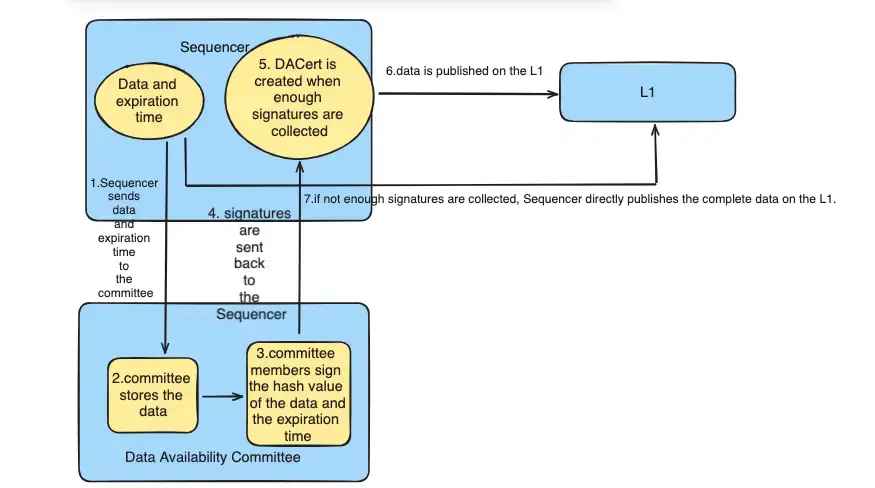
How the Sequencer and the Committee Work Together
1.Sending Data: When the Sequencer has a bunch of data ready and wants the committee to share it, it sends this data with a future date when it'll expire (like in three weeks) to all the committee members. They save this data and use the data's hash value to keep track of it.
2.Getting Signatures: After that, every committee member puts their signature on the data's hash value and the expiry date, and then sends this signature back to the Sequencer.
3.Making and Sharing DACert: As soon as the Sequencer gets enough signatures, it puts them together to make a proper Data Availability Certificate (DACert) for this data batch and shares it on the L1 blockchain. This lets the L2 AnyTrust chain work with this data.
4.Plan B: If the Sequencer doesn't get enough signatures quickly, within a few minutes, it gives up on trying to share the data through the committee. Instead, it just puts all the data directly on the L1 blockchain, like what happens on chains without AnyTrust. The L2 setup knows how to handle both ways of sharing data and will manage them right.
Conclusion - Why Nova
Arbitrum Nova has two ways to share data— the traditional way of sharing all the data through Calldata, and a new, clever way that uses a DACert to show data is there and ready to use. Nova picks the best way to share data based on what's happening in the network and how much things cost. By having a trusty Data Availability Committee (DAC), Arbitrum Nova can make sure data is always there without needing to use as much from the Ethereum mainnet. This helps make transactions cheaper and faster, which is a big plus for apps that really care about how quick and costly transactions are, like games and social media.
💡
If you would like to learn more about slang in Web3, let’s explore more in our HackQuest Web3 Glossary and check out our courses on Arbitrum Nova!